Decrypts the secret key
2. Decrypts the information,
message digest, and account holder's public key.
3. Computes and compares message
digest
· The certified
documentation is then encrypted using a secret key which is in
turn encrypted with the account holder's public key.
· The certified
documentation is then verified by the account holder by using
Merchant
registration:
· Merchant must
register with TPs that correspond to particular
account type that they wish to
honor before transacting business with customer
who share the same account types.
For example if a merchant wishes
to accept visa and MasterCard ,that
merchant may have to register
with two TPs or find a TP that represent both
· The merchant registration is similar to the account holder's registration
process.
Account
Holder(customer)ordering:
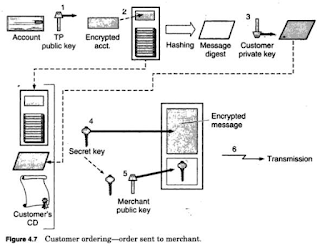
· To send a
message to a merchant the customer (account holder)must have a
copy of the merchant's public key
and a copy of the TPs public key that
corresponds to the account type
to be used.
· The order form is completed ,that customer software does the following
the public key of the TP, thus
checking the digital signature. The account
holder's software for future use in electronic commerce transaction.
Ø Encrypts account
information with the TP‟s public key.
Ø Attaches
encrypted account information to the order form
Ø Creates a
message digest of the order form and digitally signs it with the
customer's private key.
Ø Encrypts the
following with the secret key order form ,digital signature, and
customer's.
Ø Encrypts secret
key with the merchant's public key from the merchant CD.
Ø Transmits the
secret key encrypted message and encrypted secret key to the
merchant
· When the merchants software receives the order ,it does the following
Payment
authorization:
· The processing
of an order ,the merchant will need a authorize(clear) the
transaction with the TP
responsible for that particular account.
· The
authorization assures the merchant that the necessary funds or credit
limit is available to cover the
cost of the order.
· The merchant has
no access to the customer account information since it
was encrypted using the TP‟s
public key thus it is required that this
information be sent to the TP so
that the merchant can receive payment
authorization from the TP and
that the proper customer account is debited
for the transaction.
TP the following information
using encryption and digital signature process
previously described:
v Merchant's CD
v Specific order
information such as amount to be authorized order , number,
date.
v Customers ID
v Customers
account information
· After verifying
the merchant , customer, and account information the TP
would then analyze the amount to be authorized
On-Line
Electronic cash:
Overview:
· E-cash works in
the following way: a consumer opens an account with an
appropriate bank.
· The consumer
shows the bank some form of identification so that the bank
knows who the consumer is.
· The e-cash is
then stored on a PCs hard drive or possibly a PCMCIA card
for later use.
· These
transaction could all be done using public key cryptography and
digital signatures as discussed
easily.
Problem with
simple electronic cash:
· A problem with
the e-cash example just discussed is that double spending
cannot be attacked or prevent
since all cash would look the same.
· The bank sees
e-cash from a merchant with a certain serial number ,it can
trace back to the consumer who
spent it and possibly deduce purchasing
habits
· This frustrate
the nature of privacy associated with real cash.
Creating
electronic cash anonymity:
· To allow
anonymity the bank and the customer must collectively create the
e-cash and associate serial
number, whereby the bank can digitally sign and
thus verify the e-cash ,but not
recognize it as coming from a particular
consumer.
· To get e-cash
the consumer choose a random number to be used as the serial
number for the e-cash.
Preventing
double spending:
· While the
preceding process protects the anonymity of the consumer and
can identify when money has been
double spent ,it still does not prevent
consumer ,or merchant for that
matter ,from double spending.
· To create a process
to identify double spender but one that keep the
anonymity of lawful individuals
requires the use of tamperproof software
and complex cryptography
algorithms.
· The software
prevents double spending by encrypting an individuals
identity by using a random secret key generated for each piece of e-cash.
E-cash
Interoperability:
· Consumer must be
able to transact with any merchant or bank .Hence
process and security standard
must exit for all hardware and software used
in e-cash transaction.
· Interoperability
can only be achieved by adherence to algorithm and process
in support e- cash-initiate
commerce
Electronic
payment scheme:
The leading commercial electronic
payment schemes that have
been proposed in the past few
years and the companies using them .
Netscape. Netscape secure
courier electronic payment scheme which has been
selected by intuit for secure
payment between users of its quicken home
banking program and bank use
SEPP.
Microsoft: Microsoft STT is
similar to SEEP/SET in that it provides digital
signature and user authentication
for securing electronic payments. STT is
an embellished version of
Netscape's SSL security tool and is compatible
with SSL version 2.0.
Check free: check
free corporation provides online payment processing service
to major clients
To major clients, including
CompuServe, Genie, Cellular one, Delphi Internet
service corporation and Sky-Tel.
check free has also announced intension to
support all security methods that
achieve prominence inn the marketplace.
e.g., SET.
Cyber Cash :combines features from checks and is a
digital cash software system
which is used like a money order guaranteeing
payment to the merchant before
the goods shifting. Cyber Cash wants a
micropayment capabilities of 5 to 20 cents pre transaction.
VeriSign: VeriSign is
offering its digital signature technology for
authenticating as a component
separated from encryption which allows for
export of stronger
authentication. IBM is building support for digital ID into
its web browser and internet
connection secure server for AIX and OS/2.
Digi Cash: Digi Cash is a
software company whose products allow users to
purchase goods over the internet
without using accredit card. The threat of
privacy loss(where expenses can
be easily traced ) gave rice to the idea of
anonymous e-cash ,an electronic
store of cash replacement funds which can
be loaded into a smart card for
electronic purchase.
First virtual
holding:It‟s
targeting individuals and small business that want to
buy and sell on the internet but
cannot afford an extensive on-line
infrastructure. A first virtual
e-mail account and first virtual hosting system
to track and record the transfer
of information ,products , and payment for
accounting and billing purpose
,consumer and merchant can buy and sell
goods on the internet without
sensitive information such as credit card
number moving across the network.
All sensitive information is delivered
by telephone.
Commerce Net: In 1993 a group
of silicon valley entrepreneurs envisioned the
internet as a whole new model of
commerce one defined around global
access a large number of buyers
and seller many to many interaction and a
significantly accelerated pace of
procurement and development they called
this model Spontaneous commerce.
Net cash :Net cash is the
internet answer to traveler's check. To use Net cash user
must enter their checking account
or credit card numbers into an on screen
form and e-mail it to the
Net cash.
Other approach: This section
lists a few other approaches that have appeared
in the recent past.
Mondex is based on
smart card technology initially backed by the united
kingdom's West minster and
midland Banks. The electronic purse is a
handled smart card it remembers
previous transaction and use RSA
cryptography.
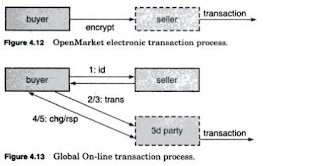
Open market handles credit
card transaction via web servers but it was planning
to provide support for debit cards
checking account and corporate purchase
order.
Global online use on-line
challenge/response. It is based on a third party
originating agreements therefore
the seller has a higher cost to enter the
market.
Wallet and such: Even in the
absence of standards(e.g., SET) vendors have
been developing system to handle
sales over the internet and companies
willing to accept that the
products are not interoperable can support business
before standard become widely deployed.




No comments:
Post a Comment