- As business activity grows on the to take into account and to address, to the stakeholders‟ satisfaction.
- Security relates to three general areas.
- Secure file/information transfer
- Secure transaction
- Secure enter price network, when used to support web commerce
- The security issue must be addressed quickly in order for companies to start investing in electronic commerce .
- There are indications that merchants are taking a wait-and –see attitude in electronic commerce on the internet until either there is a dominant standard or there is universal software that will support a variety of encryption and transaction schemes.
- The market is looking for a comprehensive solution (in a software product) that the merchants and banks can use to support all functions.
- Computer security has several fundamental goals
- Privacy: keep private document private, using encryption, passwords and access control system.
- Integrity: data and applications should be safe from modification with out the owner's consent
- Authentication: ensure that the people using the computer are the authorized users of that system.
- Availability: the end system (host) and data should be available when needed by the authorize user.
- The secure sockets layer system from Netscape communication and the secure hypertext transfer protocol from commerce net offer
- Secure means of transferring information through the internet and the world wide web.
- SSL and S-HTTP Allow the client and server to execute all encryption and decryption of web transaction automatically and transparently to the end user.
- S-HTTP (http://wwe.eit.com ) is a secure extension of HTTP developed by the commerce vet consortium.
- S-HTTP offers security techniques and encryption with RAS methods, along with Other payment protocols.
- For secure transport S-HTTP support end –to-end secure transition by incorporation cryptographic enhancements to be used for data transfer at the application level this is in contrast to existing HTTP authorization mechanisms.
- S-HTTP incorporated public-key cryptography from RSA data security in addition to supporting traditional shared secret password and Kerberos based security system.
- The RSA data security cipher used by S-HTTP utilized two Keys files encrypted by one can only be decrypted by application of the other key the recipient decrypts it with the private key.
- The secured sockets layer (SSL) protocol developed by Netscape communications is a security protocol that provides privacy over the internet.
- The protocol allows client /server application to communicate in a way that data transmissions cannot be altered or disclosed.
- Servers are always authenticated and client are Optionally authenticated
- The technology has support for key exchange algorithms and hardware tokens the strength of SSL is that it is application independent .
- HTTP, Telnet and FTP can be placed on top of SSL transparently SSL provide channel security (Privacy and authentication) through encryption and reliability through a message integrity check (secure has function).
- Netscape state that SSL aims at making the cost of such an attack greater that the benefits gained from a successful attack Thus making it a waste of time and money to perform such an attack.
- The good news is that the SSL and S-HTTP standard which will accommodate both protocols making the use of encrypted credit card transaction even easier to implement.
- A related capability is a certification authority to authenticated the public keys on which the RSA system relies .
- The goal is to assure users that public key that seems to be associated with a company actually is and is not a spurious key the authority requires applicants to prove their identify (and possibly their creditworthiness and level of certification).
- These passing the test are issued a creditworthiness and level of in which the applicant „s public key is encrypted by the authority „s private key.
- The protocols previously discussed support secure transaction. As well as more advanced secure transport capabilities.
- The secure transaction protocols discussed here are more narrowly focused.
- For secure payment, internet hardware (software vendors have made a variable of an noun cements in the past couple of years related to the support for the most popular security payment protocols. Three methods have evolved in the recent past.
- Netscape Communications Corporation and Microsoft Corporation have promoted their respective payment protocols and installed them in world wide web browsers and servers.
- SEPP have been championed by master card and Netscape and by other supporters; the American national standards institute (ANSI) is fast – tracking SEPP as a standards for the industry.
- STT (http://www.visa.com/vista-stt/index.html) was developed jointly by visa and Microsoft as methods to secure bankcard transaction over open net network.
- STT user cryptography to secure confidential information transfer, ensure payment integrity, and authenticate both merchants and cardholders confidentiality of information is ensured by the use of digital signature; cardholder account authentication is ensured and merchant credentials and interoperability is ensured by the use of specific protocols and message formats.
- At this juncture ,it appears that SET will become the industry defected standard SET has emerged recently as a convergence of the previous standards and has a lot in common with SEPP.SET is expected to be rapidly incorporated into industrial – strength “merchant ” already available from net cape , Microsoft, IBM, and other software sellers.
Security electronic payment protocol (SEPP):
- IBM , Netscape , GTE , cyber cash , and MasterCard have cooperatively developed SEEP an open , vendor natural no properties license free specification for security online transaction may of its concept were rolled into SET.
- There are several major business requirement addressed by SEPP.
- To enable confidentially of payment information.
- To ensure integrity of all payment data transmitted.
- To provider authentication that a credit holder is the legitimate owner of a card account
SEPP Process:
- To provided authentication that a merchant can accept master card bounded card payments with an acquiring member financial institution
- SEPP assume that the card holder and merchant have been communicating in order to negative terms of purchase and generate an order this process may be conducted via a www browser ; alternative this operation may be performed through the use of electronic mail, via user's review of a paper or CD-ROM catalogue or other mechanism.
- SEPP is designed to support transmit ion activity exchanged in both interactive (Online) and non-interactive (off) models.
- The collection of element involved in electronic commerce
- Cardholder: this is authorized holder of a bank card supported by on issue and register to perform electronic commerce
- Merchant : This is a merchant of goods services and or e-products who accepts payment for them electronically and line may provide selling service and are electronic delivery of items for sale (e.g., E-product)
- Acquirer: This is a (master card member) financial institution that supports merchant by providing service for processing credit card based transaction
- Certificate management system: This is a agent of one or more bankcard association's that provides for the creation and distribution of a electronic certificates for merchants acquires and cardholder.
- Bank net : this represented the existing network which interface acquires issuer and the certificate management system.
- Purchase order request
- Authorization request
- Authorization response
- Purchase order inquiry
- Purchase order inquiry response
- The merchant send an authorization request to the acquirer .the acquirer
performs the following tasks;
ü Authenticates
the merchant
ü Verifies the
acquirer/merchant relationship
ü Decrypts the
payment instruction from the buying cardholder.
ü Validate that
the buying cardholder certificate matches the account number
used in the purchase
ü Validates
consistency between merchant's authorization request and the
cardholder's payment instruction
data
ü Formats a
standard authorization request to the issues and receives the
response
ü Responds to the merchant with validates authorization request response.
SEPP
architecture:
· The SEPP buying
cardholder is represented by a cardholder workstation
which, in the initial
implementation, can be based on a World Wide Web
browser.
· Off-line
operations using e-mail or other non-interactive payment
transaction are also supported by
the protocol.
· To obtain a
certificate the buying cardholder's PC software interface with
the certificate management
system.
· The SEPP
acquirer consists of a traditional acquirer with the addition of an
acquirer gateway and a merchant
registration authority .
· It is also used
in SEPP for cardholder certificate authorization between the
certificate request server and
the issuers. Bank net provider interface based
on ISO formatted message.
Secure
Electronic Transaction(SET):
· SET is becoming
the de facto standard for security .
· The given
depicts its operation.
· The following
list depicts key function of the specification .
ü Provide for
confidential payment information and enable confidentiality of
order information that is
transmitted with payment information.
ü Ensure integrity
for all transmitted data.
ü Provide
authentication that a buyer is a legitimate user of a branded(e.g.,
Visa, MasterCard, American
Express)bankcard account.
ü Ensure the use
of the best security practice and design techniques to protect
all legitimate parties in an
electronic commerce transaction .
ü Ensure the
creation of a protocol that is neither depend on transaction port
security mechanisms nor prevent
their use.
ü Facilitate and
encourage interoperability across software and network
providers.
- Set offers buyers more security than is available in the commercial market
instead of providing merchants
with access to credit card numbers SET
encodes the numbers so only the
consumer and financial institution have
access to them.
· A similar
process takes place for the merchant at the time of the purchase
each parties SET compliant
software validates both merchant and
cardholder before any information
is exchanged.
· SET is a
combination of an application level protocol and recommended
procedures for handling credit
card transaction over the Internet.
· SET based
system will be a major impetus to the comfort level of web
shopping for both merchant and consumer.
The merchant ware that
incorporates SET will be provide online vendors
with seamless, fraud-resistant
way to handle activities ranging from
displaying goods on-line, to
settling credit card transaction via back office
link to banks.
· SET requires
that an individual possess a digital certificate for each credit
card that he or she plans to use.
· The requirement
may cause some management concerns for those user with
more than one credit card.
· Microsoft unveiled
Merchant Server ,a SET complaint internet commerce
product designed for business to
consumer business to business web sales.
· RSA data
security has introduced a developer kit that compiles with SET
.the kit helps developers build
SET capable application without building
from scratch and in supported by
vendors.
· SET does not use
full text encryption because it would require too much
processing time.
· Master card
allied with GTE to develop n initiative for electronic
certification services also under
the SET standard.
· SET goals is not
expected until 1998 or beyond there are several reason for
this.
ü Time is required
to build consensus among a critical mass of users for
credit card usage, as well as to
build a consensus among a critical mass of
usage for business-to-business
web commerce.
ü It may take
several years for technical specifications and implementations to
be installed, tested, and
debugged.
ü It may take
several years to address how web commerce should be
integrated into internal workflow
processes for businesses, for instance,
handling internal transfer
payments between business units of a company,
handling payments individuals and
businesses.
ü Two to three
years are needed to build confidence among participants that
secure electronic commerce
transactions can, in fact, be made via the
Internet.
Certificates for
authentication:
· A digital
certificate is a foodproof was of identifying both consumers, and
merchants.
· The digital
certificate acts like a network version of a driver‟s license- it is
not credit, bat used in
conjunction with any number of credit mechanisms, it
verifies theusers identity.
· Digital
certificates, which are issued by certificates authorities such as
VeriSign and cyber trust, include
the holder‟s name, the name of the
certificates authority a public
key for cryptographic use and a time limit for
the use of the certificates.
· The certificates
typically includes a class, which indicates to what degree it
has been verified.
· For example,
VeriSign digital certificates come in three classes.
· Nortel also
offers digital certificates as part of its ensues Internet security
software.
· Both Hewlett –
Packard company and IBM have announced their intentions
to use Entrust with their
electronic commerce and security products.
· One of the
issues affecting the industry, however, is interoperability. The
document certification practice
statement issued by VeriSign proposes
interoperability approaches, but the outcome was unknown at press time.
Security on web
servers and enterprise networks:
· There are two
general techniques are available;
v Host security
consideration
v Enterprise
network security
· Host based
security capabilities; these are means by which each and every
Computer on the system in
mode(more) impregnable.
· Security
watchdog system which guard the set of internal interconnected
Systems, communication between
the internal world must be funneled
Through, these system.
· These watchdog
systems that deal with security within an organizations
own enterprise networks are
called firewalls.
· A firewall
allows a business to specify the level of access that will be
afforded to networks users.
In general, both
methods are required.
v An internet site
can set up an anonymous FTP site that allows any outside
user to access files at the site
(anonymous FTP is very useful to companies
that wish to place documentation
in the public domain; it also can be used to
allow users to download
software).
v This could be as
a start alone system which is updated only by off-line
means (eg., load a diskette),or
by a physically separate post (eg, console
port); or, it could be a system
outside the firewall (but still residing on the
overall organization's networks)
called a bastion.
v The firewall
comes into play if the FTP system located on the
organization's networks, for case of updating.
Host security
considerations:
· Host security is
a discipline that goes back to the 1960‟s main frame were
perhaps endowed with more
rigorous security capabilities than their
successors . Naturally ,security
comes at a price including the following
ü The Financial resource
spent in acquiring the constituent element such as
packet filters proxy server log
hosts ,vulnerability detection tools, smart
cards ,and so on.
ü The staff time
spent configuring these tools identifying and correcting
security holes and training the
users about the new tools.
Venues to host
infraction:
· In a stand alone
host environment ,host access can be restricted to logging
in at the console through the
serial port card or over a restricted dialup line
in a network environment a web
server, for example access is typically
available from a variety of
sources.
ü Individual
accessing information on the organization host(Web/HTTP)
ü Individual
accessing the organization host transparently(e.g., NFS,NIS)
ü Individual
interrogating the organization host(e.g., via ping, finger, dig,
nslookup )
ü Individual
running programs on the organization host(rsh , x)
ü Individual
taking and leaving things (mail,UUCP,FTP,rcp)
ü Individual
understanding networks logins(rlogin,Telnet)
· The majority of
communication utilities in host were designed in the 1970
and 1980 without a high regard
for security at a time the goal way easy
network access .
· Anyone with
administrative powers can reconfigure a host‟s IP address and
create specific accounts in order
to masquerade as another host and user on
the network.
Host Based
security tools include the following:
v Monitoring and
logging tools
v Filtering Tools
v Vulnerability
detection tools
Web security
concerns include the following
· Server side
security which involves protecting hosts running the WWW
servers themselves
· Client side
security which relates to security issues involved in requesting
WWW service.
· Confidentiality
which aims at guaranteeing the privacy of information
transmitted across the network between clients and servers.
Some basic
precautions for the server are the follows
· The http demon
server should be executable only by root and is to be
typically invoked only at
execution time.
· All files and
directories in the server directory structure should be owned by
root.
· Do not allow
user to install scripts in this directory
· Remove all
ability for remote logins such as rlogin or telnet
· Remove all
nonessential compiler and programming tools that might be
used by attackers to create or
run programs on the server.
Enterprise
Network Security:
· A firewall (also
called a secure Internet Gateway ) supports communication
based security to screen out
undesired communication which can cause
havoc on the host
· Host based
security is a critical element of overall computer security
although is does not scale easily
,nonetheless it must be employed.
· Ideally an
administrator use all available tools including host security and
communication gateway security .
· It is like
having two lacks on a door both methods should be used for
increased assurance .the firewall
deployment in the enterprise network must
support the following
capabilities ,
ü All traffic
between the inside and outside must transmit through the
firewall.
ü Only authorized
traffic based on the security policy is allowed transit the
firewall itself must be immune to
penetration .
· Firewalls act as
a single focus for the security policy of the organization and
support advanced authentication
techniques such as smart card and one
time password.
· Firewall are
typically configured to filter traffic based on one of two design
policies.
ü Permit unless
specifically denied this is weaker because it is impossible to
be aware of all the numbers
network utilities you may need to protect
against specifically this
approach does not protect against new internet
utilities .
ü Deny unless
specifically permitted this is stranger because the administrator
can start off with a blank permit
list and add only those function that are
explicitly required.
· There are some
variation in firewall architecture which modulated both the
security level as the cost and
complexity of the hardware .
· There are two categories of firewall
IP and or TC/UDP
datagram(packet)filters(including screening
routers)which parse/filter
traffic based on some combination of IP host and
Network address ,IP protocol
,Port number, and possibly other values.
ü Application
layer protocol gateways (also known as proxy servers )which
are intermediately hosts that
accept incoming request for communication
services and make the appropriate calls on the client behalf.
Electronic
Payment and Electronic payment schemes:
· E-Cash is a form
of an electronic payment system where a certain amount of
money is stored on a client‟s
device and made
accessible for online transaction
.
· Stored-value
card – A card with a certain amount of money that can be used
to perform the transaction in the
issuer store .
Internet
Monetary payment and security Requirement:
· For consumer and
merchant to be able to trust one another ,Prevent
transmitted payment information
from being tampered with and complete
transaction with any valid party
,the following issues need to be addressed:
ü Confidentiality
ofpayment information
ü Integrity of
payment information transmitted via public networks
ü Verification
that an accountholder is using a legitimate account
ü Verification
that a merchant can accept that particular account
ü Interoperability
across software and network provider.
Confidentiality
of payment information:
· Payment
information must be secure as it travels across the internet ,without
security payment information
could be picked up by hackers as the router
communication line or host level
possibly resulting in the production of
counterfeit card or fraudulent
transaction.
· There are two
encryption methods used symmetric cryptography and
asymmetric cryptography.
· Symmetric
cryptography or more commonly called secret key cryptography,
use the same key to encrypt and
decrypt a message.
· A commonly used
secret key algorithm is the Data Encryption
Standard(DES)
·
Asymmetric
cryptography ,or public key cryptography ,use two distinct keys :a public key
and a private key.
· This allows
multiple senders to receiver who uses the private key to
decrypted it .The assurance of
security is dependent on the receiver
protecting the private key.
· For merchants to
use secret key cryptography ,they would each have to
administer individuals secret key to all their customer and provide these
keys through some secure channel
.This channel complex from an
administrative perspective.
· This process
,the customer generate a random number used to encrypt
payment information using DES.
The DES encrypted payment information
and the encrypted DES key are
then transmitted to the merchant.
· To decrypt the
payment information the merchant first decrypt the DES key
then use the DES key to decrypt the payment information .
Payment information Integrity :
· Payment
information sent from consumer to merchants includes order
information, personal data and
payment instruction .The information is
modified ,the transaction may no
longer be accurate.
· To eliminate
this possible source of error or fraud, an, arithmetic algorithm
called hashing. The hash
algorithm generates a value that is unique to the
payment information to be
transferred.
· A helpful way to
view a hash algorithm is as a one way public cipher, in
that
Ø It has no secret
key
Ø Given a message
digest there is no way to reproduce the original
information.
Ø It is impossible
to hash other data with the same value.
· To ensure the
integrity the message digest is transmitted with the payment
information .The receiver would
then validate the message digest by
recalculating it once payment
information is received .
· If the message
digest does not calculate the same value sent the payment
information is assumed to be
corrupted and is therefore discarded.
· To rectify the situation the message digest is encrypt using a private key of
the sender (customer).This
encryption of a message digest is called a digital
signature.
A digital signature is created by
using public key cryptography ,it is
possible to identify the sender
of the payment information .The encryption
is done by using the private key
of a public /private key pair this means only
the owner of that private key can
encrypt the message digest.
· Note that the
roles of the public/private key pair in the digital signature
process are the reverse of that
used in ensuring information confidentiality.
· A digital
signature however ,does not authorize a particular customer to use
the monetary account information
located in the payment.
Account holder
and merchant authentication:
· Similar to the
way card accounts are stolen and used today, it is possible for
a person to use a stolen account
and try to initiate an electronic commerce
transaction .
· A way to secure
this link is by use of a trusted third party who could
validate the public key and
account of the customer this third party could be
one of many organization
,depending upon the type of account used.
· For example if a
credit card account were used the third party could be one
of the major credit card
companies ;if a checking account were used ,the
third party could be the federal
clearinghouse or some other financial
institution .
· Merchants would
then decrypt the public key of the customer and ,by
definition of public key
cryptography ,validate the public key and account
of the customer. For the
preceding to transpire ,however, the following is
assumed
Ø The public
key(s) of the third party (i.e.)is widely distributed
Ø The public key(s)
of the third party(i.e.) is highly trusted on face value
Ø The third
party(i.e.) issue public keys and accounts after receiving some
proof of an individual's identity.
Interoperability:
· For electronic
commerce to take place ,customer must be able to
communicate with any merchant.
· Interoperability
is then achieved by using a particular set of publicly
announced algorithm and process
in support of electronic commerce.
4.2 Payment and
purchase order process:
Overview:
· For an
electronic payment to occur over the internet the following
transaction/process must occur.
Ø Account holder
registration
Ø Merchant
registration
Ø Account holder
(customer) ordering
Ø Payment
authorization
Account holder registration :
Account holder must register with
a third party (TP)that corresponds to a
particular account type before
they can transact with any merchant.
· In order to
register ,the account holder must have a copy of the TP‟s public
key of the public/private key
set.
· To register the
account holder will most likely be required to fill out a from
requesting information such as
name, address, account number, and other
personal information when the form is completed the account holder software will do the following.
1.Create and attach the account holder's public key to the form
2.Generate a message digest from
the information
3.Encrypt the information and
message digest using a secret key
4.Transmit all times to the TP
· When the TP receives the account holder's request, it does the following
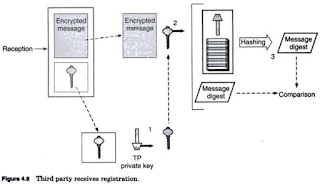 PAGE-2
PAGE-2




No comments:
Post a Comment